- In-Stock Tumor Cell Lines
- Human Orbital Fibroblasts
- Human Microglia
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Valvular Interstitial Cells
- Human Thyroid Epithelial Cells
- C57BL/6 Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Alveolar Macrophages
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Lung Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Retinal Muller Cells
- Human Articular Chondrocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
- Human Kidney Podocyte Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
Heart research often hinges on the ability to recapitulate key functional aspects of the human heart in vitro. A critical tool enabling this work is the use of high-quality cardiomyocytes—the specialized muscle cells responsible for cardiac contraction and electrical signaling. When applied in well-characterized in vitro systems, these cells support the development of physiologically relevant cardiac models for cardiac disease modeling and early-stage drug discovery.
What Are Cardiomyocytes and Why Do They Matter?
Cardiomyocytes are the heart’s contractile cells, characterized by high mitochondrial density and specialized electrophysiological properties (e.g., action potentials and calcium handling) that enable rhythmic contraction. These features make cardiomyocytes indispensable for in vitro cardiac disease modeling, where experimental fidelity is essential for capturing clinically relevant phenotypes. Cardiac models based on functional cardiomyocytes have been shown to reduce false-negative and false-positive signals during preclinical screening, thereby enhancing translational confidence.
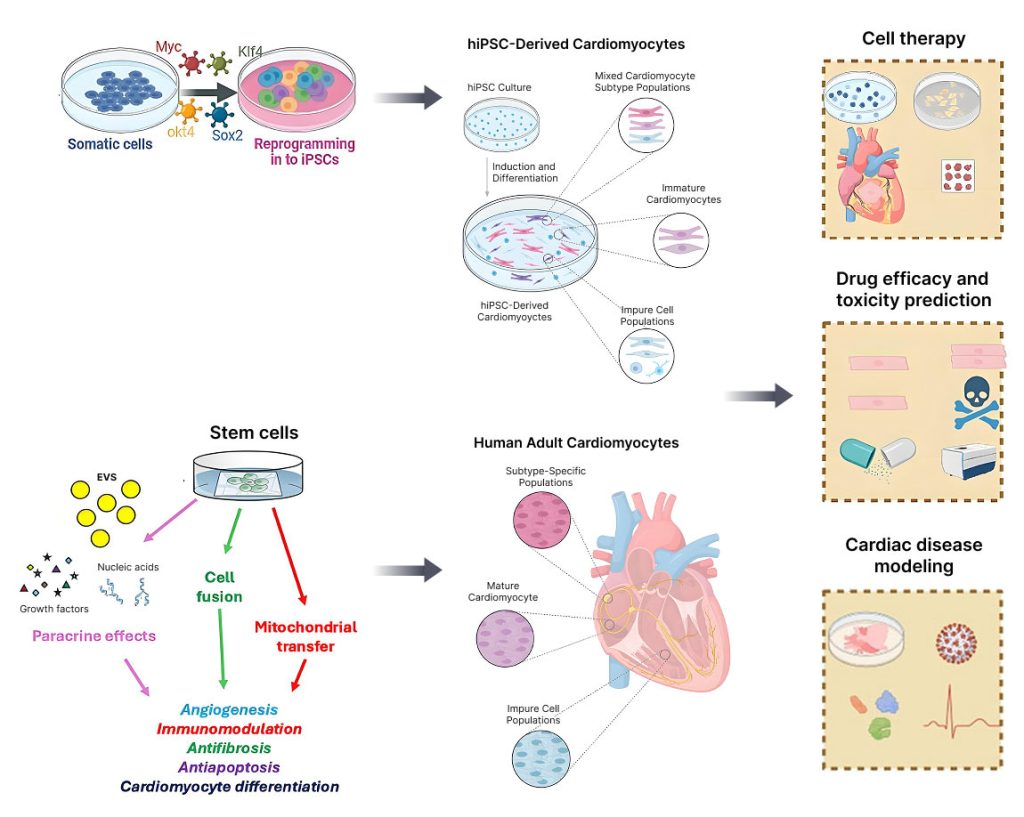
Human iPSC-Derived Models: Bridging In Vitro Systems and Human Biology
The use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to generate human cardiomyocytes represents a major advance in cardiac model development. AcceGen’s HighQC™ Human iPSC-Derived Atrial Cardiomyocytes and HighQC™ Human iPSC-Derived Ventricular Cardiomyocytes enable region-specific cardiac disease modeling, supporting in vitro cardiac models that capture key aspects of human cardiac electrophysiology and contractile behavior.
These cardiomyocyte-based cardiac models are well suited for:
- Disease-relevant electrophysiology studies
- Drug-induced cardiotoxicity assessment
- Mechanistic investigations that support improved clinical translation and development success rates
Primary and Stem Cell–Based Models: A Spectrum of Cardiac Tools
Complementing the iPSC-derived models, AcceGen also provides human cardiomyocytes differentiated from other stem cell sources, as well as animal-derived cardiac stem cell models. Human Primary Cardiac Myocytes offer high-fidelity representations of native cardiac function in vitro, preserving essential physiological characteristics for short-term functional assays and advanced cardiac disease modeling.
Together, these cardiomyocyte platforms form a scalable toolkit of cardiac models, allowing researchers to select the most appropriate in vitro system based on experimental objectives, throughput requirements, and desired physiological fidelity.
Why Use Cardiomyocytes for Drug Screening?
Cardiac safety remains a critical challenge in drug development. Compared with conventional immortalized cell lines, cardiomyocyte-based cardiac models in vitro provide enhanced physiological relevance, enabling earlier identification of cardiotoxic risk. By improving model fidelity at the preclinical stage, these systems support more informed decision-making and may contribute to higher clinical development success rates by reducing late-stage attrition.
Researchers can explore AcceGen’s full portfolio of cardiomyocytes for in vitro cardiac models by searching “cardiomyocytes” on the AcceGen website at: https://www.accegen.com/search/?q=cardiomyocytes

Copyright - Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are AcceGen™ All Rights Reserved – Full details of the use of materials on this site please refer to AcceGen Editorial Policy – Guest Posts are welcome, by submitting a guest post to AcceGen you are agree to the AcceGen Guest Post Agreement – Any concerns please contact marketing@accegen.com