- In-Stock Tumor Cell Lines
- Human Orbital Fibroblasts
- Human Microglia
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Valvular Interstitial Cells
- Human Thyroid Epithelial Cells
- C57BL/6 Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Alveolar Macrophages
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Lung Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Retinal Muller Cells
- Human Articular Chondrocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
- Human Kidney Podocyte Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
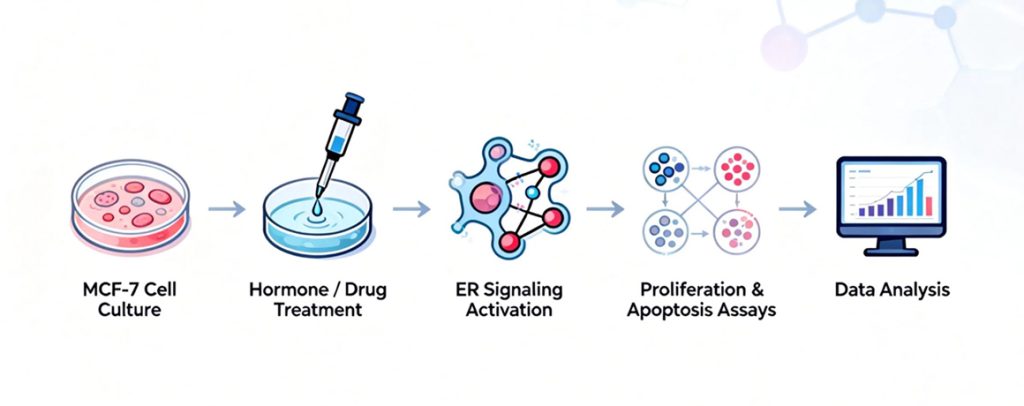
Introduction to the MCF-7 Cell Line
MCF-7 cells are derived from a pleural effusion of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma, representing a well-established, estrogen-responsive breast cancer model which is particularly valuable for researching estrogen positive breast cancer, receptor-mediated transcriptional regulation, and therapeutic response mechanisms.
Hormone Receptor Profile and Biological Significance
A defining feature of MCF-7 is its classification as an estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) positive breast cancer model. These cells express both ER and PR. This receptor status provides a biologically relevant platform for exploring how hormonal cues influence tumor growth, differentiation, and survival.
The presence of functional receptors allows researchers to examine:
- Estrogen-dependent proliferation
- Ligand-regulated gene transcription
- Receptor crosstalk and downstream signaling
- Endocrine therapy responses
Role of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in MCF-7 Cells
Among the hormone receptors expressed in MCF-7, estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) plays a dominant regulatory role. ERα functions as a ligand-activated transcription factor that orchestrates gene expression programs governing cell cycle progression, metabolic adaptation, and survival pathways.
Upon estrogen stimulation, estrogen receptor alpha undergoes conformational activation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation. The receptor complex then binds to estrogen response elements (EREs) within genomic DNA, triggering transcription of target genes involved in:
- Cellular proliferation
- Anti-apoptotic signaling
- Differentiation processes
- Therapeutic sensitivity
Experimental Utility of MCF-7 Cells
Endocrine Signaling Studies
Researchers frequently employ MCF-7 to dissect estrogen-mediated signaling networks, transcriptional regulation, and receptor modulation dynamics. The cell line’s sensitivity to hormonal stimulation allows for precise evaluation of receptor activation and inhibition events.
Drug Discovery and Screening
Due to their ERα-dependent proliferation profile, MCF-7 breast cancer cells are widely used in the development and evaluation of:
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Receptor degraders
- Targeted signaling inhibitors
Resistance Mechanism Modeling
Endocrine resistance remains a major clinical challenge. MCF-7 cells provide a controlled platform for studying adaptive signaling changes, receptor reprogramming, and compensatory survival pathways.
Importance of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Antibody Tools
Accurate characterization of ERα expression and activity is essential for reliable experimental outcomes. High-specificity reagents such as the estrogen receptor alpha antibody are therefore critical components of receptor-focused studies.
In MCF-7 cells, ERα antibodies are routinely applied in:
- Western blot analysis for protein quantification
- Immunofluorescence for subcellular localization
- Immunocytochemistry for receptor visualization
- Flow cytometry for expression profiling
The use of a validated estrogen receptor alpha antibody enables researchers to monitor receptor dynamics, assess ligand-dependent modulation, and evaluate treatment-induced signaling alterations.
MCF-7 Cells as a Translational Research Model
Beyond basic studies, MCF-7 breast cancer cells serve as a highly translationally relevant model for:
- Understanding hormone-driven tumor progression
- Optimizing endocrine therapeutic strategies
- Identifying predictive biomarkers
- Evaluating receptor-targeted interventions
Their proven reproducibility and biological relevance establish MCF-7 as a benchmark model, essential for advancing our understanding of ERα signaling in estrogen-positive breast cancer.

Copyright - Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are AcceGen™ All Rights Reserved – Full details of the use of materials on this site please refer to AcceGen Editorial Policy – Guest Posts are welcome, by submitting a guest post to AcceGen you are agree to the AcceGen Guest Post Agreement – Any concerns please contact marketing@accegen.com